Physiologic Pigmentation
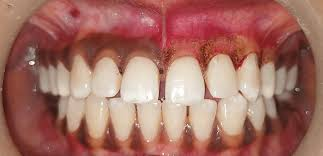
Physiologic Pigmentation
Physiologic pigmentation refers to the natural coloration of the skin, hair, and eyes that is determined by genetics and is influenced by various factors such as hormones, age, and sun exposure.
Introduction:
Physiologic Pigmentation In the skin, the primary pigment responsible for color is melanin, which is produced by cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes are located in the basal layer of the epidermis and produce melanin in response to various stimuli, including UV radiation from the sun. Melanin is then transferred to neighboring keratinocytes, which are the cells that make up the majority of the epidermis. The amount and type of melanin produced can vary from person to person and is determined by genetics.
In addition to melanin, other factors such as the blood vessels in the skin and the amount of fat in the dermis can also contribute to skin color. For example, the skin may appear pink or red due to the presence of blood vessels, and the skin may appear yellow or pale due to the presence of fat.
Physiologic pigmentation can also refer to the natural coloration of the hair and eyes. The color of the hair is determined by the type and amount of pigment produced by the hair follicles, while the color of the eyes is determined by the amount and type of pigment in the iris, as well as the scattering of light by the tissues in the eye.
Overall, physiologic pigmentation refers to the natural coloration of the body’s tissues and is influenced by a variety of factors including genetics, hormones, age, and sun exposure.
What is Physiologic Pigmentation:
Physiologic pigmentation refers to the natural coloration of the skin, hair, and eyes that is determined by genetics and is influenced by various factors such as hormones, age, and sun exposure.
In the skin, the primary pigment responsible for color is melanin, which is produced by cells called melanocytes. Melanocytes are located in the basal layer of the epidermis and produce melanin in response to various stimuli, including UV radiation from the sun. Melanin is then transferred to neighboring keratinocytes, which are the cells that make up the majority of the epidermis. The amount and type of melanin produced can vary from person to person and is determined by genetics.
In addition to melanin, other factors such as the blood vessels in the skin and the amount of fat in the dermis can also contribute to skin color. For example, the skin may appear pink or red due to the presence of blood vessels, and the skin may appear yellow or pale due to the presence of fat.
Physiologic pigmentation can also refer to the natural coloration of the hair and eyes. The color of the hair is determined by the type and amount of pigment produced by the hair follicles, while the color of the eyes is determined by the amount and type of pigment in the iris, as well as the scattering of light by the tissues in the eye.
Overall, physiologic pigmentation refers to the natural coloration of the body’s tissues and is influenced by a variety of factors including genetics, hormones, age, and sun exposure.
Physiologic Pigmentation Pros:
There are several benefits to physiologic pigmentation, which is the natural coloration of the skin, hair, and eyes. Some of the pros of physiologic pigmentation include:
- Protection from the sun: Melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of the skin, hair, and eyes, provides some protection from the harmful effects of UV radiation from the sun. Melanin absorbs and disperses UV radiation, helping to prevent DNA damage and skin cancer.
- Natural beauty: Many people find natural skin, hair, and eye colors attractive, and physiologic pigmentation allows people to have these natural colors without the need for artificial dyes or treatments.
- Easy maintenance: Unlike artificial dyes or treatments, physiologic pigmentation does not require regular maintenance or touch-ups, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Personal identity: Physiologic pigmentation is an important part of an individual’s identity and can be a source of pride and self-esteem.
Overall, physiologic pigmentation has many benefits and is an important aspect of an individual’s appearance and identity.
Cons:
There are generally not many cons associated with physiologic pigmentation, which is the natural coloration of the skin, hair, and eyes. However, some people may experience negative consequences due to societal standards and preferences for certain skin, hair, and eye colors. For example, certain skin tones may be subject to discrimination or prejudice, and some people may feel pressure to conform to certain standards of beauty. In addition, some people may be unhappy with their natural hair or eye color and may wish to change it through artificial means such as dyes or treatments.
Another potential disadvantage of physiologic pigmentation is that it may not provide sufficient protection from the sun in certain situations. For example, people with lighter skin tones may be more prone to sunburn and skin damage due to their lower levels of melanin. In these cases, it is important to use sunscreen and protective clothing to prevent sunburn and skin damage.
Overall, while physiologic pigmentation is generally not associated with negative consequences, it is important for people to recognize and respect the diversity of skin, hair, and eye colors and to take steps to protect their skin from the harmful effects of the sun.
If you want to get amazing benefits by using this link
Conclusion:
In conclusion, physiologic pigmentation refers to the natural coloration of the skin, hair, and eyes that is determined by genetics and is influenced by various factors such as hormones, age, and sun exposure. Physiologic pigmentation has many benefits, including protection from the sun, natural beauty, easy maintenance, and personal identity. While there are generally not many cons associated with physiologic pigmentation, some people may experience negative consequences due to societal standards and preferences for certain skin, hair, and eye colors, and some people may be unhappy with their natural hair or eye color. It is important for people to recognize and respect the diversity of skin, hair, and eye colors and to take steps to protect their skin from the harmful effects of the sun.











Post Comment